Create IAM Role for Lambda Post
Objective: Create the IAM role LambdaInsertStudentRole for the Lambda function
insertStudentData, granting permissions to write data to the DynamoDB tablestudentData, send emails via AWS SES, log data to CloudWatch, and support potential interactions with S3 and CloudFront.
The function insertStudentData performs:
- Stores student information (Student ID, Full Name, Class, Date of Birth, Email) into the DynamoDB table
studentDatavia the PutItem operation. - Sends a confirmation email to the student’s email address via AWS SES.
This role needs:
- Permissions to log data to CloudWatch (
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole). - Permissions to read and write data to DynamoDB (
AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess). - Permissions to send email via SES (
AmazonSESFullAccess). - Permissions for S3 and CloudFront (
AmazonS3FullAccess,CloudFrontFullAccess) for potential future features.
Note:
AmazonS3FullAccessandCloudFrontFullAccessare not currently used in the code, but are retained for future functionalities (e.g., saving files to S3 or managing CloudFront).
Detailed Steps
Below are the detailed steps to create the IAM role LambdaInsertStudentRole:
1. Access the AWS Management Console
-
Open your browser and log in to the AWS Management Console with your AWS account.
-
In the search bar at the top of the page, type IAM and select Identity and Access Management (IAM).
-
Ensure you are in the correct AWS region (e.g.,
us-east-1), check in the top right corner.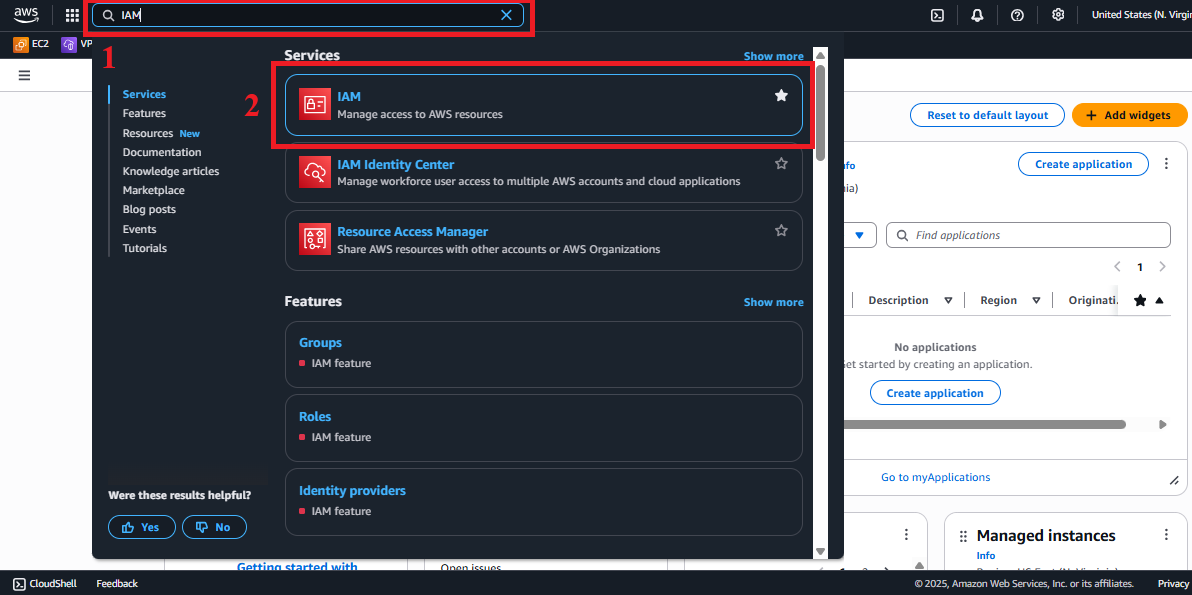 Figure 1: AWS Console interface with the IAM search bar.
Figure 1: AWS Console interface with the IAM search bar.
2. Navigate to the Roles Section
-
In the IAM interface, find the left-hand navigation menu.
-
Select Roles to view the list of IAM roles. If no roles exist, the list will be empty.
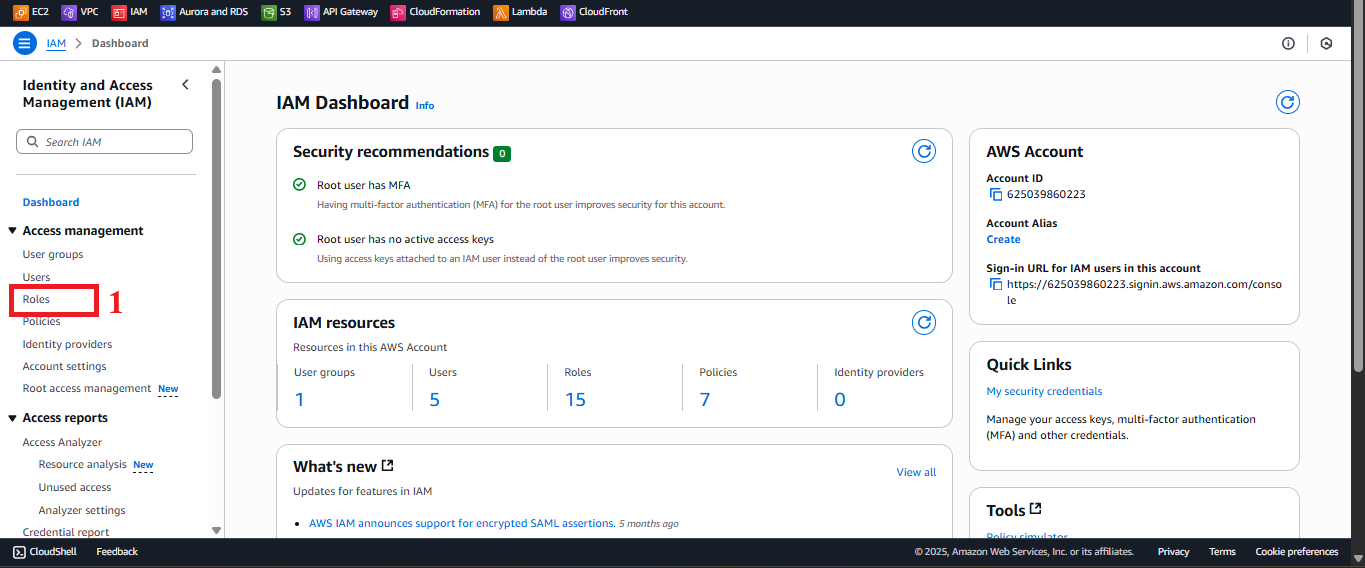 Figure 2: Navigation menu with the Roles option.
Figure 2: Navigation menu with the Roles option.
3. Start the Role Creation Process
-
In the Roles interface, click the Create Role button in the top-right corner.
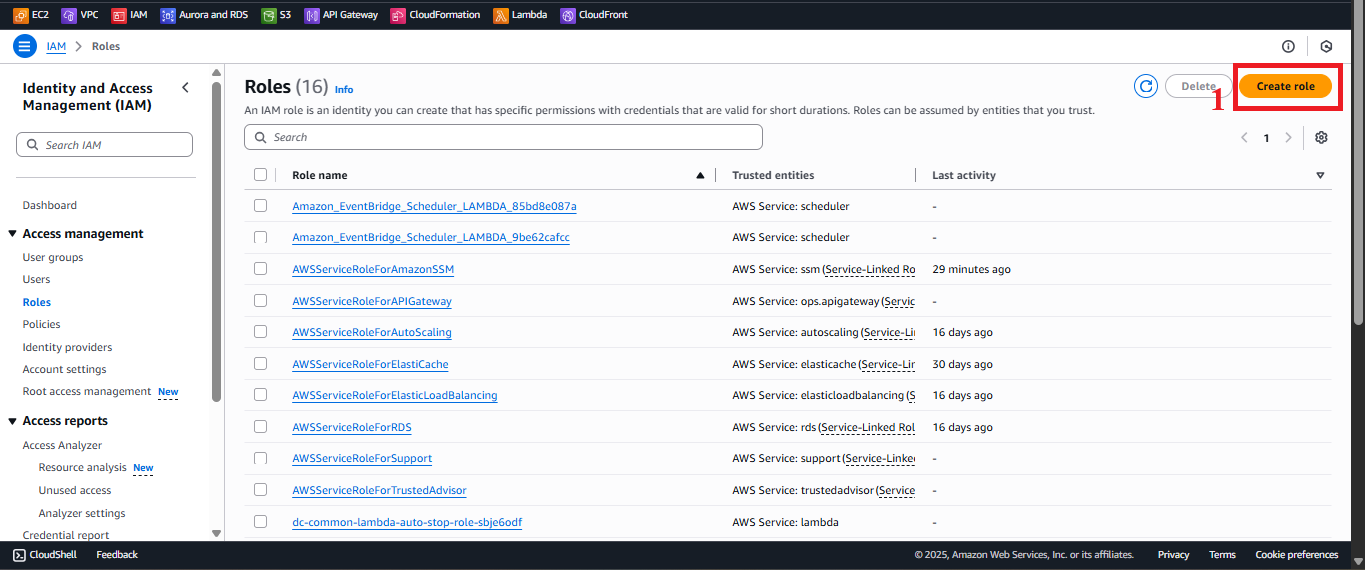 Figure 3: Create Role button in the Roles interface.
Figure 3: Create Role button in the Roles interface.
4. Choose Trusted Entity Type
-
In the Select trusted entity section, choose AWS Service to specify that the role is for an AWS service.
-
In the Use case section, select Lambda from the list of services.
-
Click Next to move to the permission configuration step.
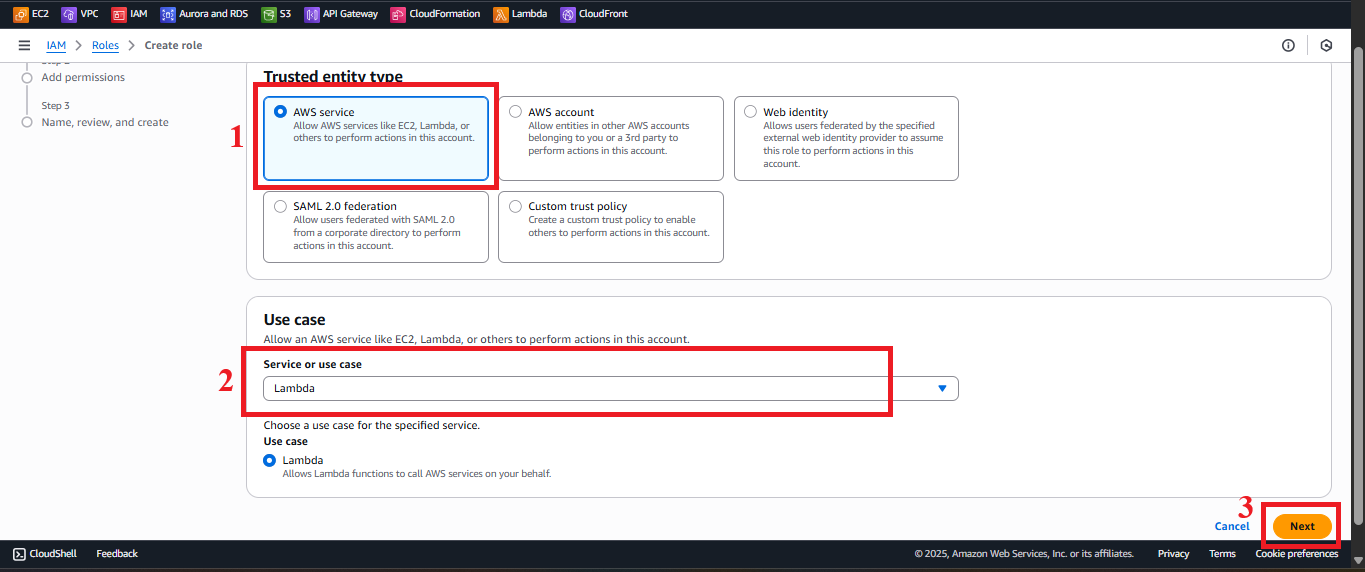 Figure 4: Choosing AWS Service and Lambda in Use case.
Figure 4: Choosing AWS Service and Lambda in Use case.
5. Grant Permissions to the Role
-
In the Permissions section, add the following policies:
-
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole:
- Type
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRolein the search bar. - Select the AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole policy.
Description: Allows the Lambda function to log to CloudWatch for monitoring and debugging.
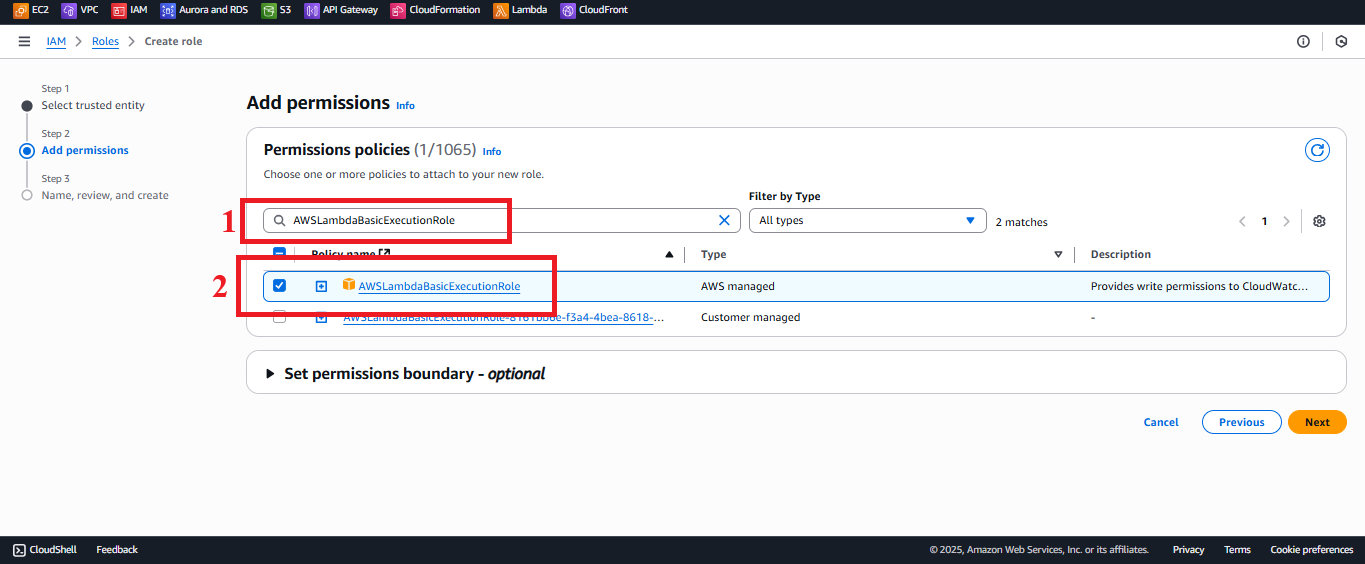 Figure 5: Selecting the AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole policy.
Figure 5: Selecting the AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole policy. - Type
-
AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess:
- Type
AmazonDynamoDBFullAccessin the search bar. - Select the AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess policy.
Description: Grants read and write access to DynamoDB, including the PutItem operation required for the
insertStudentDatafunction.
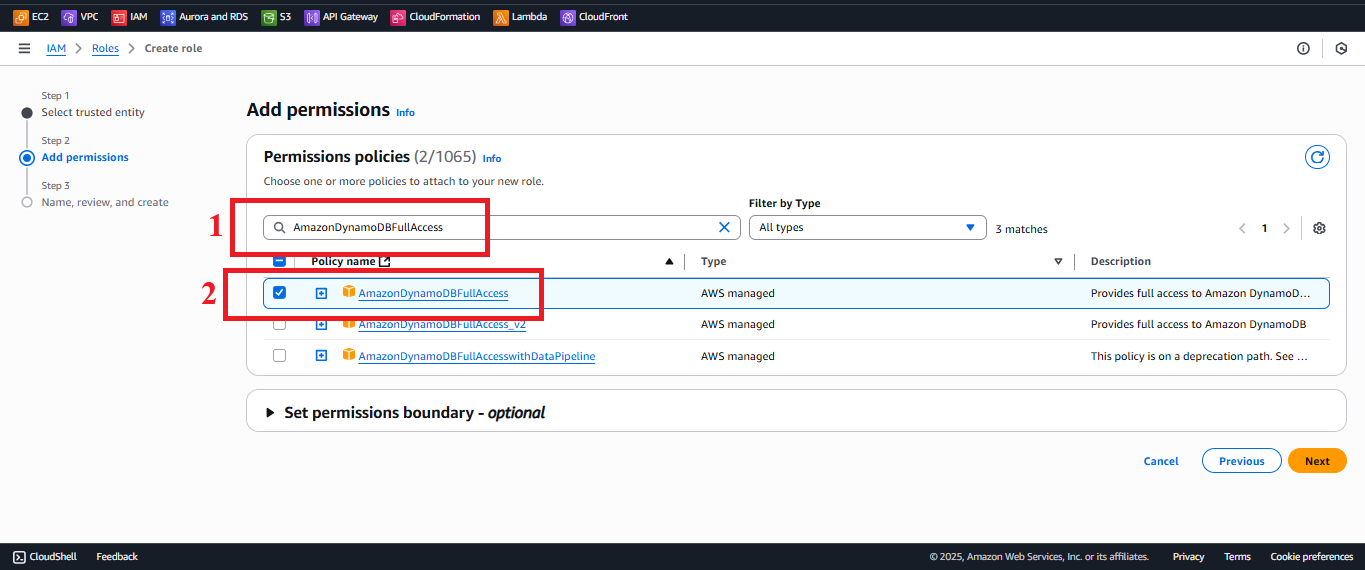 Figure 6: Selecting the AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess policy.
Figure 6: Selecting the AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess policy. - Type
-
AmazonSESFullAccess:
- Type
AmazonSESFullAccessin the search bar. - Select the AmazonSESFullAccess policy.
Description: Grants permission to send emails via SES to send confirmation notifications (e.g., to
nguyentribaothang@gmail.com).
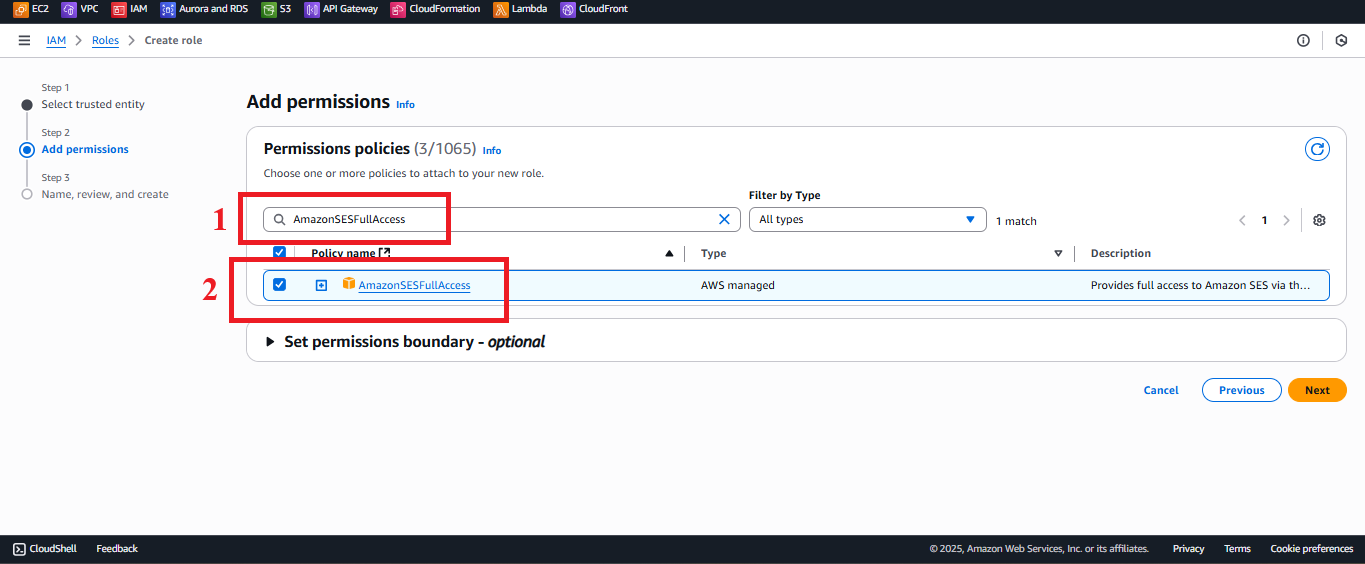 Figure 7: Selecting the AmazonSESFullAccess policy.
Figure 7: Selecting the AmazonSESFullAccess policy. - Type
-
AmazonS3FullAccess (optional):
- Type
AmazonS3FullAccessin the search bar. - Select the AmazonS3FullAccess policy.
Description: Grants read, write, and manage S3 buckets for potential future features.
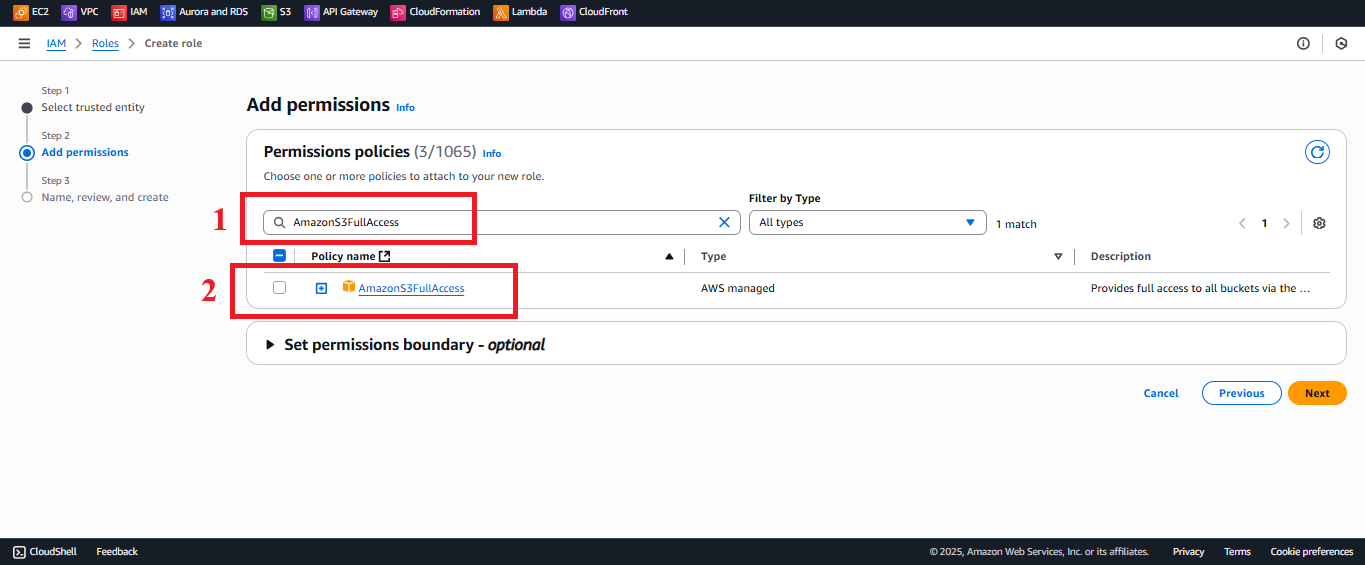 Figure 8: Selecting the AmazonS3FullAccess policy.
Figure 8: Selecting the AmazonS3FullAccess policy. - Type
-
CloudFrontFullAccess (optional):
- Type
CloudFrontFullAccessin the search bar. - Select the CloudFrontFullAccess policy.
Description: Grants permission to manage CloudFront distributions for potential future features.
- Type
 Figure 9: Selecting the CloudFrontFullAccess policy.
Figure 9: Selecting the CloudFrontFullAccess policy. -
-
Verify the list of Permissions policies to ensure it includes:
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRoleAmazonDynamoDBFullAccessAmazonSESFullAccessAmazonS3FullAccessCloudFrontFullAccess
-
Click Next.
6. Name and Review the Role
-
In the Role details section:
- Role Name: Enter
LambdaInsertStudentRole.Note: The name must match exactly with the Lambda function configuration for
insertStudentData. - Description (optional): Enter a description, e.g., “IAM role for Lambda function insertStudentData, granting write access to DynamoDB, sending emails via SES, logging to CloudWatch, and supporting S3/CloudFront.”
 Figure 10: Enter role name and description.
Figure 10: Enter role name and description. - Role Name: Enter
-
Double-check:
- Trusted entity: AWS Service (Lambda).
- Permissions:
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole,AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess,AmazonSESFullAccess,AmazonS3FullAccess,CloudFrontFullAccess.
-
Click Create Role.
7. Check Role Creation Status
-
After clicking Create Role, you will return to the Roles list.
 Figure 11: Click Create Role to finalize the creation.
Figure 11: Click Create Role to finalize the creation. -
Find the LambdaInsertStudentRole role. If successful, you should see the message: “Role LambdaInsertStudentRole created”.
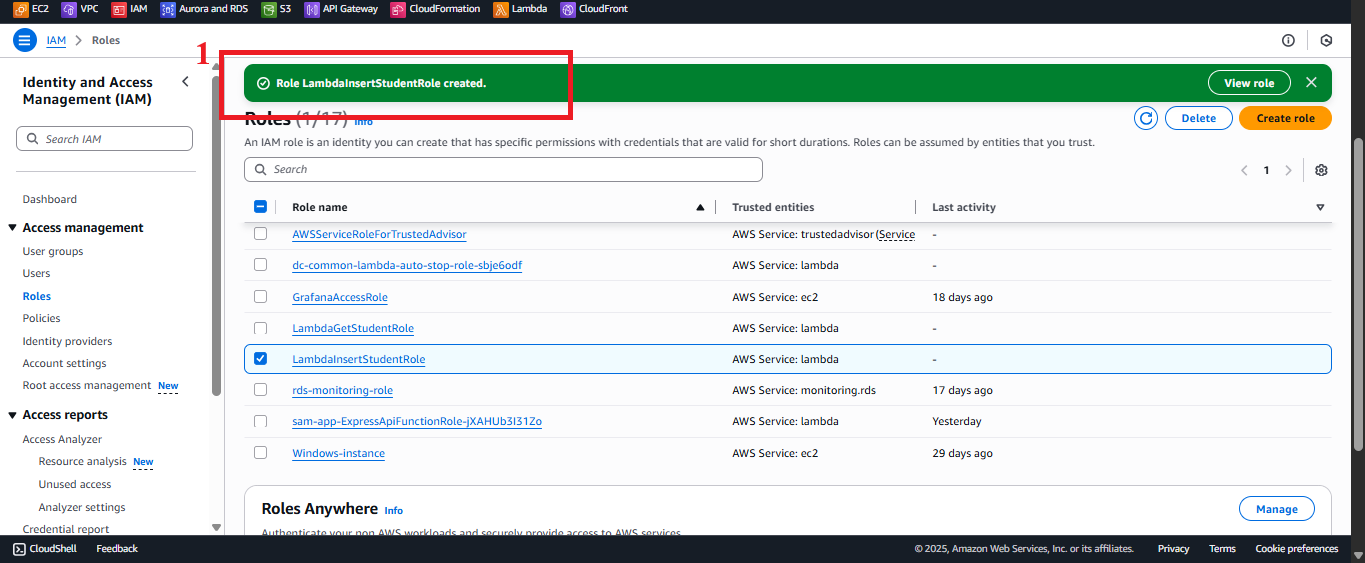 Figure 12: Success message for the LambdaInsertStudentRole creation.
Figure 12: Success message for the LambdaInsertStudentRole creation. -
Click on LambdaInsertStudentRole to view details:
- ARN: Record the ARN (e.g.,
arn:aws:iam::your-account-id:role/LambdaInsertStudentRole) to use when configuring the Lambda function. - Policies: Verify that the correct policies are attached.
- ARN: Record the ARN (e.g.,
-
If the role does not appear, refresh the page or check the steps again.
Important Notes
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Role Name | Must be LambdaInsertStudentRole (case-sensitive) to match the Lambda function. Incorrect names will cause execution errors. |
| DynamoDB Permissions | AmazonDynamoDBReadOnlyAccess does not support PutItem. Use AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess to allow PutItem on the studentData table. |
| S3 and CloudFront | AmazonS3FullAccess and CloudFrontFullAccess are not currently used, but are retained for potential future functionalities (e.g., saving files to S3 or managing CloudFront). Delete if unnecessary to comply with least privilege. |
| Check Early | Record the ARN and verify the role in IAM before configuring the Lambda function to ensure proper setup. |
| Error Handling | If you encounter an “Access Denied” error, check AWS account permissions (iam:CreateRole, iam:AttachRolePolicy) or contact your administrator. If the function reports AccessDenied, check the DynamoDB policy. Use CloudTrail or IAM Access Advisor to pinpoint the issue. |
| AWS Region | Ensure the AWS region (e.g., us-east-1) is consistent with other services (DynamoDB, Lambda, SES). Check in the top right corner of the AWS Console. |
Practical Tip: Always verify the role and ARN immediately after creation to confirm correct configuration before integrating with the Lambda function.
Conclusion
The IAM role LambdaInsertStudentRole ensures that the Lambda function insertStudentData has the necessary permissions to write data to DynamoDB, send emails via SES, and log data to CloudWatch, while supporting future extensions with S3 and CloudFront. With AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess, the function operates efficiently and securely in a serverless application.
Next Step: Proceed to Create IAM Role for DynamoDB Backup to set up the role for data backup!